Using ADB To Access Android Device
Android Debug Bridge (ADB) is not the choice for the novice user out there, and why should it be? It is totally a command line based tool, it lacks the user friendliness that would be a GUI and has some serious pre requisites as well in the form of the SDK to be downloaded and the Java SDK as well. That said, the ADB tool is the lifeline of Android devices and is not meant for tinkering with as far as novice users are concerned. That in no way means that users can’t take advantage of some of the basic commands that are safe and quick to perform. Below we will try and break down some of the few basic commands you can make use of on your Android device, but before we proceed with that, you should see our guide on what is ADB and how to install it on your Android Device. So if you haven’t already been intimidated by the guide we just referred you to, let’s get out hands dirty.
To copy a file from PC to device.
There are two ways you can go about this.
- Navigate to the location of the file and in that folder, hold down the Shift key, press the Right mouse button and select Open Command Window Here. Or you can simply open terminal or command prompt and navigate to the location of the folder manually. Once the command window or terminal is running, enter the following command:
adb push example.apk /data/app
Replace example.apk with the actual name of the file and /data/app with a location where the file will be placed in the device. adb push basically needs to be followed by the name of the file and then the folder on your device. - Incase you’re not already in the directory where the file is placed on the computer, open command prompt or terminal and enter the following command:
adb push C:\addictivetips\example.apk /data/app
Replace C:\addictivetips\example.apk with the full path of your file and /data/app with where you want the file to be pushed.
Please note that pushing APK files as described above to the /data/app folder installs the app as well. If you do not want to install the file, simply push it to another location.
To copy a file from Android device to PC.
Again, there are two ways you can go about this. To pull the file from the device, you need to identify the destination folder where the file will be copied, and point to the target folder, that is location of the file as well. Or if you want, you can navigate to the destination folder inside command prompt or terminal and issue the pull command from there without having to point at a folder in the command. Here’s how.
adb pull /data/app/example.apk
or
adb pull /data/app/example.apk C:\addictivetips
ADB Shell based commands.
In ADB Shell, you can execute Linux based commands to explore your device’s contents, as you would explore your drives on a Linux based PC without having to use the ADB tag over and over again. It is also important to be in ADB Shell if you want to access the system folders via ADB on a rooted device. How can you enter the shell mode? With the device plugged in, enter the following command:
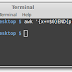
adb shell
If you’re rooted, you will see a # symbol, indicating that you are now in shell mode and have all superuser rights. If your device is not rooted, you will get the $ symbol.
You can use the list (ls) command for example, to view the folders you have on your device or change directories as you would on your Linux desktop.
For a complete list of ADB commands, you can use the command “adb help” or head over to the official Android Developers page.
'via Blog this'